A malfunction removable storage device can do the same harm to your PC. For instance, once the SyQuest drive attached to my PC was broken. The system kept looking for the device and cartridge, and as a result, my PC ran like a 8088. To resolve the problem, I simply unplugged the SyQuest drive.
To troubleshoot a slow PC, you should find out where the problem is. After checking the BIOS and hardware, you should check your system resources by using Resource Meter. While your usual applications are running, go to Start/Program/Accessories/System Tools/Resource Meter.
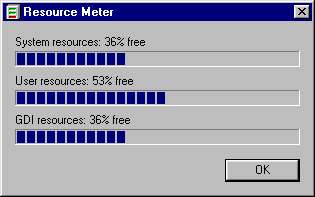
If the System and User Resources are slow, you can reconfigure your cache and free up your hard disk space as a remedy, which will be discussed later. If your graphical device interface resource is slow, you may need a video accelerator.
To check whether your older applications or drivers degrade the system performance, open the System Control Panel, select the Performance tab, and check if the system is configured for optimal performance.
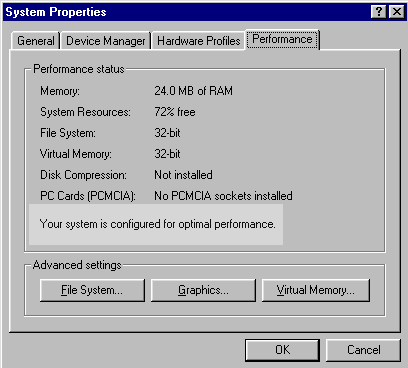
The dialog box will tell you whether your system is loaded with real-mode drivers. If so, comment out the loading of real-mode drivers in Config.sys. From Start open Run, then type Sysedit to open System Editor. Several system configuration files will open. Bring Config.sys to the front and put "rem" (remark) in front of any line that loads a real-mode driver. For example, the following statement is remarked because it loads a real-mode CD-ROM driver.
rem ---------------------- MTM ATAPI CD-ROM ----------------------
rem DEVICE=C:\MTM\MTMCDAI.SYS /D:MTMIDE01
On the System Control Panel/Performance, click on the button File System to check whether your computer role is selected properly.
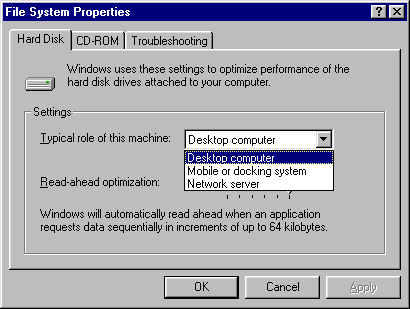
Some Windows expert suggests that when your PC has more than 16 meg of RAM, you should select the role of your computer as a network server even though the computer is a workstation. However, if this configuration causes the system slowing down, you should choose "Desktop" instead because your PC may run some RAM-consuming applications.
Further, some applications manage their own cache. Just like VM, cache requires free hard disk space for storage. If the original location is almost full, you should re-assign a new home for cache. Different applications have different ways to alter the cache location. For instance, in Netscape Preferences should be edited but in Internet Explorer, Options (Why don't all programs use the same name for the same thing? Well, if you rename something, it is an invention rather than copying).
If so, would a large block size solve this problem? Yes, but it will waste a lot of disk space. For example, if you assign 64K as the block size and you save a 4K file, the small file will occupy the entire block and 60K is wasted. To solve the fragmentation problem, You should optimize your hard drive once a while. Optimization will put all files into contiguous blocks and thus reduce the access time.
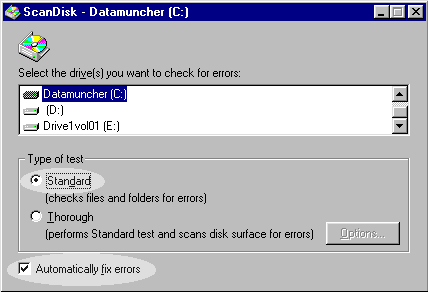
Before optimizing your hard drive, you should run ScanDisk first because any file or disk error will hinder the system from defragmenting. First, you must quit all applications, then open ScanDisk from Program/Accessories/System Tools. There are two options: Standard and Thorough. A standard scandisk will check for file and folder errors only while a thorough scandisk will detect the preceding errors plus the disk error. A thorough scan will take a much longer time. Use Standard unless you suspect that you hard disk has errors. Also make sure the box "Automatically fix errors" is checked.
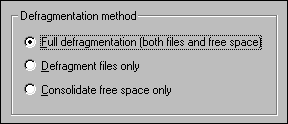
After ScanDisk is complete, run Disk Defragmenter in the Program/Accessories/System Tools for optimization. You may also use a shortcut by pulling up Run from Start and type defrag in the command field. At the degragmenter dialog box, click Advanced to unveil more options. There are three choices in Disk Defragmenter, namely, Full Defragmentation, Defragment files only, and Consolidate free space only. You should select the first choice. Defrag files only may cause new files become more scattered because it leaves gaps between files though the existing files are put back together. Consolidate free space only does not gather existing file fragments. Rather it just eliminates any space before and after each fragment. To really optimize your hard disk, a full defragmention, which both re-organizes fragmented files and eliminates space between files, is a must. Although this procedure takes a longer time, it worths the wait.
If Scandisk or defrag goes into a loop i.e. the process completes certain percent and jumps back to the beginning over and over again, probably some new data are written to the disk. Even if you does not run any application, some StartUp or screen saver, especially Push Technology, which sends you updated news frequently, is doing something spontaneously. To ensure a smooth optimization, you should disable your StartUp and Screen Saver.
To disable your StartUp:
- Right click Start and choose Open.
- Open Program and create a new folder called temp.
- Move all files from StartUp to temp.
To shut down your screen saver or push channel:
- Open Control Panel from My Computer.
- Open Display.
- Select Screen Saver tab.
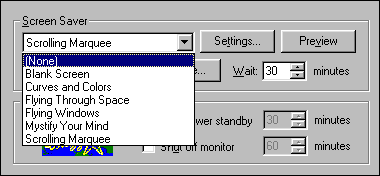
- Pull down the choices for screen saver and select None.
Now you can reboot your computer and proceed to Scandisk and defrag. Afterwards, reverse the preceding changes.
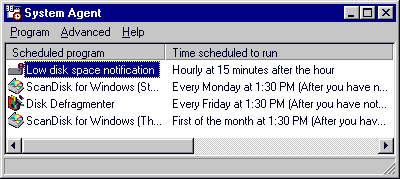
You can perform Scandisk and Defrag in Norton Utilities. The equivalent names in Norton are Norton Disk Doctor and Speed Disk. Also, you can automate the Scandisk and Defrag procedures if you have installed Microsoft Plus. In Microsoft Plus there is a scheduler called System Agent for you to set run Scandisk and Defrag periodically. After Microsoft Plus is installed, System Agent can be accessed through Program/Accessories/System Tools. When System Agent is open, select Schedule a New Program from Program. The procedure is self-explanatory.
Please notice that you must leave your PC on and idle at the scheduled date and time in order to let the automatic ScanDisk and Defrag run. If you don't want to do that or you don't want to spend extra money to buy Microsoft Plus, you can configure your PC to run ScanDisk upon startup. The procedure is as the following:
- First create a shortcut of ScanDisk in the Startup folder. Right click Start and choose Open. Then click open Program and then StartUp.
- Click open the folder StartUp and right click in a blank space. Choose New/ShortCut. In the command field type SCANDSKW /A /N. /A switch will instructs Scandisk to check all local and fixed hard drives. /N will start and close Scandisk automatcally. Click Next and then click Finish.
- Right click on the new ScanDisk shortcut. Click Find Target. The ScanDisk Utilities will be located.
- Click open ScanDisk. Makes sure Stardard scan rather than Thorough scan is selected, otherwise your PC will take forever to start up. Also check the box "Automatically fix errors." Then click the button Advanced.
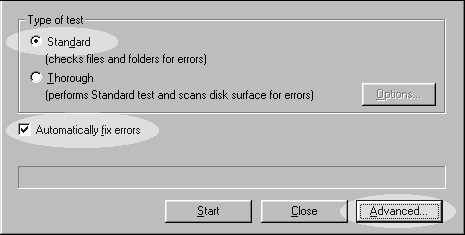
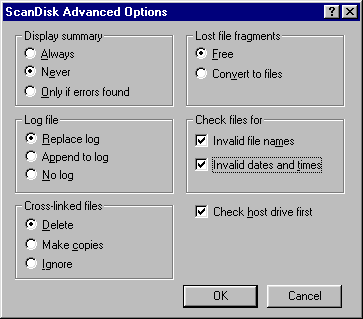
- Select the options as indicated in the following figure. Then click Run. If you choose Close, the modifications will not be saved.
To remediate the problem, quit all applications, use Find to locate temporary files (*.tmp) and delete them. It is important that you must first close all applications because some temp files may be in use by opening apps.
You may add these lines to your autoexec.bat. It will automatically clean up your temp files when the PC starts up.
set temp=C:\temp
if exist c:\temp\*.tmp del c:\temp\*.tmp
Deleting temp files in Windows 98 is easier. Open Accessories/System Tools/Maintenance Wizard. The wizard askes you which kinds of temp files you want to delete regularly.
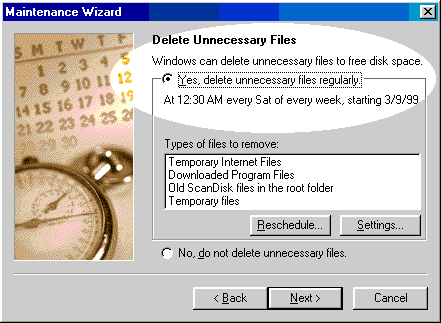
You can use some third-party products such as Clean Sweep or Remove It to do the job, but they cost money, of course. Fortunately, a freeware named Clean System Directory is available in www.ozemail.com.au/~kevsol/sware.htm. As its name implies, the freeware can scan your hard drive for unused DDLs and move them to a backup folder. You can delete those DDLs immediately or wait for several weeks. If all programs can run smoothly, then you can permanently erase them. If a program complains that a DDL is missing, then go to the backup folder and restore the DDL.
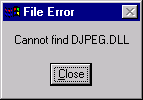
It is important to notice that if you have multiple operating systems in multiple partitions, you should ask Clean System Directory to scan your startup disk only. For instance, if you have Chinese Windows 95 in C: drive, English Windows 98 in D: drive, Windows NT in E: drive, and you run Clean System Directory under Windows 95, then in the dialog box you should check C: and deslect D: and E: (see the following figure). If you select all of them, Clean System Directory may move the DDLs used by Windows 98 and Windows NT.
If you are unable to clean up your system, consider to wipe out Windows and reinstall everything from scratch. Actually, the best solution to this problem is prevention. Try to be selective about what you put into your PC. Always do a custom install so that you can include only the components that you really need.
In Windows 98, removing startup is easier. Open Accessories/System Tools/Maintenance Wizard. The wizard askes you which startup you want to exclude.
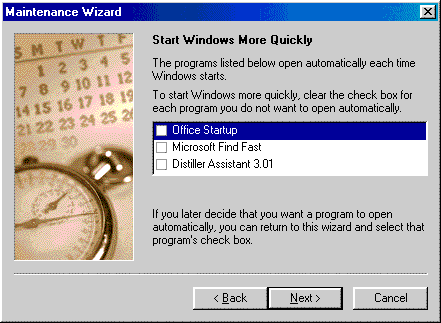
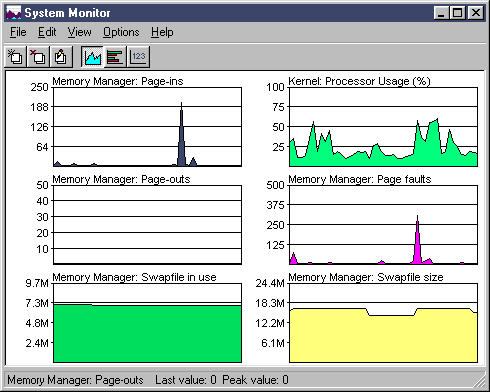
Processor Usage indiciates how busy your CPU is. Swapfile size and page faults show you how much paging is done for gaining virtual memory. If the former equals to or exceeds 80 percent, you definitely need a more powerful CPU. If the latter group is high, then you need to add more RAM to reduce paging.
Although it is easier to upgrade the CPU only, it is advisable to upgrade both the motherboard and the CPU. An older motherboard may not get the most out of your new CPU.
If you need to upgrade RAM, don't bother to use software to "double" your RAM. Although RAM Doubler works very well on the Mac platform, on the PC side many RAM compression software packages cannot deliver what they promise. Therefore you should install more physical RAM instead.
Further, RAM and CPU combined are not the only factor for a PC's performance. A slow input/output bus, a slow hard drive, or other slow peripherals may be the bottleneck. In the older version of Norton Utilities, the benchmark function of the System Information tests the CPU/RAM, the hard disk, and the overall system seperately. However, in the newer version it tests only the CPU and RAM. You should read the hard drive manual or some other objective benchmark report to find out the speed of your hard disk. You may consider to use a SCSI hard drive as well as other SCSI devices to replace your IDE interface devices because the former is significantly faster than the latter.